First, what is plc?
PLC is an intelligent controller, which is a computer (PC). PLC is a programmable controller.
The definition is: an electronic system for digital computing operations designed for industrial environments. It uses a class of programmable memory for its internal memory program, performing user-oriented instructions such as logic operations, sequence control, timing, counting and arithmetic operations, and controlling various types of machinery through digital or analog input/output. Or the production process. The PLC and its associated peripherals should be designed to be easy to integrate with industrial controls and easy to expand.

Second, PLC features (advantages)
1. High reliability and strong anti-interference ability
2, full-featured, complete equipment, strong applicability
3, easy to learn, easy to operate
4, the system design, easy maintenance, easy to transform, simple construction
5, small size, lighter, low energy consumption
Third, the application area
Due to the integrated control of organic electricity, PLC storage logic replaces external wiring, and the data computing ability is strong. In addition, the enhancement of communication technology is widely used, such as steel, petroleum, chemical, electric power, building materials, machinery manufacturing, automobile, transportation, culture and entertainment. In other industries, the following controls can be achieved.
1. Logic control of switching quantity
It replaces the traditional relay circuit, realizes logic control and sequence control, and can be used for control of single equipment, multi-machine group control and automatic assembly line. Such as injection molding machines, printing machines, bookbinding machinery, combination machine tools, grinding machines, packaging production lines, electroplating lines and so on.
2, analog control
In the industrial production process, there are many continuous changes, such as temperature, pressure, flow, liquid level and speed are analog quantities. In order for the programmable controller to process the analog quantity, it is necessary to implement A/D conversion and D/A conversion between analog (Analog) and digital (Digital). PLC manufacturers produce matching A/D and D/A conversion modules to make programmable controllers for analog control.
3, motion control
The PLC can be used for the control of circular motion or linear motion. From the perspective of the control mechanism configuration, the early use of the switching I/O module to connect the position sensor and the actuator is now generally using a dedicated motion control module. For example, single or multi-axis position control modules that can drive stepper motors or servo motors. The products of all major PLC manufacturers in the world have almost all motion control functions, which are widely used in various machines, machine tools, robots, elevators and other occasions.
4, process control
Process control refers to closed-loop control of analog quantities such as temperature, pressure, and flow. As an industrial control computer, PLC can program a variety of control algorithm programs to complete closed-loop control. PID regulation is a much used adjustment method in general closed-loop control systems. Large and medium-sized PLCs have PID modules, and many small PLCs currently have this function module. PID processing is generally a dedicated PID subroutine. Process control has a wide range of applications in metallurgy, chemical, heat treatment, boiler control and other occasions.
5, data processing
Modern PLC has functions such as mathematical operations (including matrix operations, function operations, logic operations), data transfer, data conversion, sorting, table lookup, bit manipulation, etc., which can complete data collection, analysis and processing. These data can be compared with reference values ​​stored in the memory to perform certain control operations, or can be transferred to other smart devices using communication functions, or printed and tabulated. Data processing is typically used in large control systems, such as unmanned flexible manufacturing systems; it can also be used in process control systems such as large control systems in the paper, metallurgical, and food industries.
6, communication and networking
PLC communication includes communication between PLCs and communication between PLCs and other intelligent devices. With the development of computer control, the factory automation network has developed rapidly. Each PLC manufacturer attaches great importance to the communication function of PLC and has launched their own network systems. The newly produced PLCs all have communication interfaces, and communication is very convenient.
Fourth, the structure of the PLC and the role of each part
The structure of the programmable controller is various, but the general principle of its composition is basically the same, and the structure is based on the microprocessor. It usually consists of a central processing unit (CPU), memory (RAM, ROM), input and output unit (I/O), power supply, and programmer.
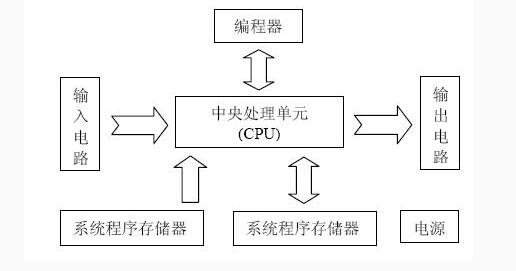
1. Central processing unit (CPU)
As the core of the entire PLC, the CPU plays the role of the general commander. The CPU is generally composed of a control circuit, an arithmetic unit, and a register. These circuits are typically packaged on a chip of an integrated circuit. The CPU is connected to the storage unit and the input/output interface circuit through an address bus, a data bus, and a control bus. The functions of the CPU are as follows: reading instructions from memory, executing instructions, taking an instruction, and processing interrupts.
2. Memory (RAM, ROM)
The memory is mainly used to store system programs, user programs, and work data. The memory that stores the system software is called the system program memory; the memory that stores the application software is called the user program memory; the memory that stores the work data is called the data memory. Commonly used memories are RAM, EPROM, and EEPROM. The RAM is a random memory storage user program that can perform read and write operations, and generates a user data area, and the user program stored in the RAM can be easily modified. The RAM memory is a high-density, low-power, and inexpensive semiconductor memory that can be used as a backup power source with a lithium battery. When power is lost, the stored information can be effectively maintained. EPROM and EEPROM are read only memories. Use these types of storage to solidify hypervisors and applications.
3. Input and output unit (I/O unit)
The I/O unit is actually an interface component that transfers input and output signals between the PLC and the controlled object. The I/O unit has good electrical isolation and filtering. The input devices connected to the PLC input interface are various switches, buttons, sensors, and the like. The output control devices of the PLC are often solenoid valves, contactors, relays, and the relays are AC and DC type, high voltage type and low voltage type, voltage type and current type.
4. power supply
The PLC power supply unit includes the power supply of the system and the backup battery. The function of the power supply unit is to convert the external power supply into an internal working voltage. There is a regulated power supply in the PLC for powering the CPU unit and I/O unit of the PLC.
5. Compiler
The programmer is the most important peripheral of the PLC. The programmer can be used to send the user program into the PLC's memory. You can also use the programmer to check the program, modify the program, and monitor the PLC's working status. In addition to this, the PLC can be programmed with a personal computer by adding the appropriate hardware interface and software package to the personal computer. Using a microcomputer as a programmer, you can directly program and display ladder diagrams.
Fifth, the working principle of PLC
The PLC adopts the working mode of cyclic scanning. In the PLC, the user programs are stored in order. The CPU starts executing the program from the first instruction, and then returns to the first one after encountering the terminator, so that the cycle continues cyclically.
The scanning process of PLC is divided into internal processing, communication operation, program input processing, program execution, and program output. The time required to scan the entire process is called the scan cycle. When the PLC is in the stop state, only internal processing and communication operation services are performed. When the PLC is in the running state, it performs cyclic scan work from internal processing, communication operation, program input, program execution, and program output.
1. Input processing
Input processing is also called input sampling. At this stage, the state of the end of all input terminals is sequentially read, and the read information is stored in the corresponding image register in the memory. The input image register is refreshed here. Then enter the program execution phase. When the program is executed, the input image register is isolated from the outside world. Even if the input signal changes, the contents of the image register will not change. The information can only be read in the input processing stage of the next scan cycle.
2. Program execution
According to the principle of PLC ladder program scanning, according to the steps of first left and then right first up and down, the program is executed step by step. A program jump instruction is encountered, and the jump address of the program is determined according to whether the jump condition is satisfied. When the user program involves the input/output status, the PLC reads the status of the corresponding input terminal acquired in the previous stage from the input image register, reads the corresponding image register from the output image register, performs logical operation according to the user program, and saves In the relevant device register. For each device, the contents of the device image registers are subject to change as the program progresses.
3. Output processing
After the program is executed, the output image register, that is, the state of the Y register in the device image register, is dumped to the output latch in the output processing stage, and the power amplifier circuit is driven through the isolation circuit to output the output terminal to the outside. Control signals that drive external loads.
Air Insulated Switchgear,Sentron Protection Device,3000 Amp Switchgear,Outdoor Switchgear Enclosure
Shandong Shunkai electrical equipment co., LTD. , https://www.chinasdsk.com